Thyroid Artery Embolization
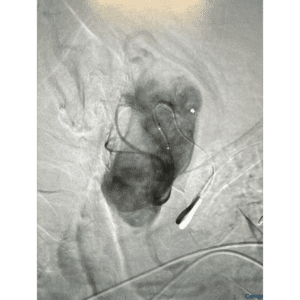
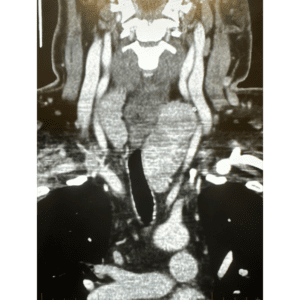
Thyroid artery goiter embolization or TAE is a image guided non surgical outpatient procedure that is an alternative treatment option to prevent removal of the thyroid gland. Ussually, TAE is used to shrink significant enlargements of the thyroid glang (known as goiter) which is frequent in both men and women. Women are at a higher risk, especially during pregnancy.
In general, goiters can be categorized as diffuse, nodular or multinodular goiter. Diffuse goiter is usually not localized to a certain region and tends to involve the entire gland. Nodular goiter occurs when there is only one nodule in the thyroid gland, and multinodular goiter occurs when the thyroid gland has multiple nodules.
According to thyroid hormone levels, goiters can be classified as toxic or non-toxic. Toxic goiters refer to those that have excessive thyroid hormone levels, while non-toxic goiters are associated with normal thyroid hormone levels.
Goiter Causes
Goiter can be caused by a variety of factors:
Goiter Diagnosis
Physical examination is the most common way of diagnosing a thyroid goiter. A physician can detect them in the neck by touch.
The next easiest and fastest test is an ultrasound, commonly used when results of the physical examination are inconclusive. Ultrasound helps distinguish thyroid related issues from other masses in the neck.
If the nodules are large enough, there can be deviation of the aiway (“wind pipe”) or of the esophagus leading to shortness off breath or issues with swalowing food. This can be further studies by additional imaging such as a CT scan. This can also demostrate extension of the thyroid into the chest.
Goiter Treatment Options
Currently the gold standard treatment for a thyroid goiter is surgical removal. The downside is that complete removal of the thyroid gland will result in lifelong hormone replacement. In addition, an open surgery has risks which include nerve injury, electrolyte imbalances, infection, and other post-operative complications. The use of radioactive iodine is another option which also carries the risk of causing lifelong hormone supplementation. Percutaneous thermal ablation (i.e laser ablation, RFA, microwave) is another less invasive option, however, if the volume of tissue being treated exceeds 30 mL, it is likely it wont work or it may require multiple sessions. This is the main reason why non-surgical thyroid artery embolization (TAE) has become an effective, minimally invasive, and safer alternative for a thyroid goiter.
Thyroid Artery Goiter Embolization Procedure
Thyroid Artery Embolization is a medical technique used to treat conditions that result from excessive production of thyroid hormones such as nodules, goiter and hyperthyroidism. The procedure consists of intentionally blocking (embolizing) one or more of the arteries that provide blood flow to the thyroid gland. This helps limit the hormone production and reduce the size of goiter or nodules thus reducing symptoms.
The procedure is performed under imaging called fluoroscopy. You will be given medications to keep you comfortable and relaxed during the procedure. Access to the arteries feeding the thyroid is through a small puncture site in either both wrists or the groin. Your doctor inserts a catheter through this puncture site and once it is in position, tiny particles (embolic agents) are injected into the thyroid arteries. These particles block the blood vessels suppling blood to the thyroid gland. Contrast dye and imaging techniques are used to confirm the blood supply as been adequately cut off (embolized). At the end of the procedure, the catheter is removed and the puncture sites closed and bandage is applied.
After a recovery of several hours, most patients will be able to go home the same day but some may be required to stay overnight.
Advantages of thyroid artery embolization include:
· Minimally invasive
· Typically preserves some level of thyroid function
· No scarring of the neck
· Reduced symptoms
· Quick recovery
Thyroid Artery Embolization (TAE): Results
Within six months of undergoing TAE, patients report excellent outcomes. This is a timeline of what to expect:
Patients who underwent TAE and that have received a prior RFA reported a high satisfaction rate six months after the procedure, and also considered recommending other patients with multinodular goiter to undergo the procedure themselves.
Other resources:
THE SERVICES LISTED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR GENERAL INFORMATION PURPOSES ONLY AND DO NOT INCLUDE ALL SERVICES OF FLORIDA INTERVENTIONAL SPECIALISTS. WHILE WE STRIVE TO KEEP THE INFORMATION UP TO DATE AND CORRECT, WE MAKE NO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, ABOUT THE CONTENT, COMPLETENESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY, LEGALITY, SUITABILITY OR AVAILABILITY, WITH RESPECT TO THE SERVICES CONTAINED ON THIS WEBSITE.
